Welcome to our latest update on the six-month journey testing home battery storage using sodium batteries. As a significant departure from the popular LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and Lithium NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries, our sodium batteries offer unique advantages and characteristics worth exploring.
Overview of Our Sodium Batteries
Our sodium batteries are configured as 48V 75Ah units. They exhibit a wide voltage range, spanning from 28V to 62V, closely resembling lead-acid batteries rather than lithium-based counterparts. This extensive voltage range simplifies the determination of the State of Charge (SOC) by the inverter, negating the necessity for a Battery Management System (BMS) cable to the inverter. This is a significant advantage, as previous experiences with Pylontech lithium batteries highlighted the susceptibility of BMS cables to failure, leading to bloated and broken batteries.
Testing with Various Charging Equipment
To thoroughly evaluate the performance and compatibility of our sodium batteries, we tested them with a range of charging equipment, including basic inverters, off-grid AC chargers, and hybrid solar inverters.
- Basic 1500W 48V to 240V Inverter
- Performance: The sodium batteries performed reliably with this basic inverter setup, providing stable power conversion from 48V DC to 240V AC. The simplicity of the system highlighted the ease of SOC management without the need for additional BMS integration.
- EDECOA 3000W Off-Grid AC Charger with MPPT Solar Controller
- Integration and Efficiency: This combination allowed us to leverage solar energy effectively. The MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controller optimized solar input, and the sodium batteries maintained excellent charge retention and discharge rates. This setup proved to be highly efficient for off-grid applications.

3. GROWATT SPA3000 3kW Grid-Tied Battery Charger
- Grid Interaction: With the GROWATT SPA3000, our sodium batteries seamlessly integrated into a grid-tied system. The charger efficiently managed grid interactions, ensuring smooth transitions between solar power, battery storage, and grid supply. This setup demonstrated the potential for sodium batteries in reducing grid dependency.
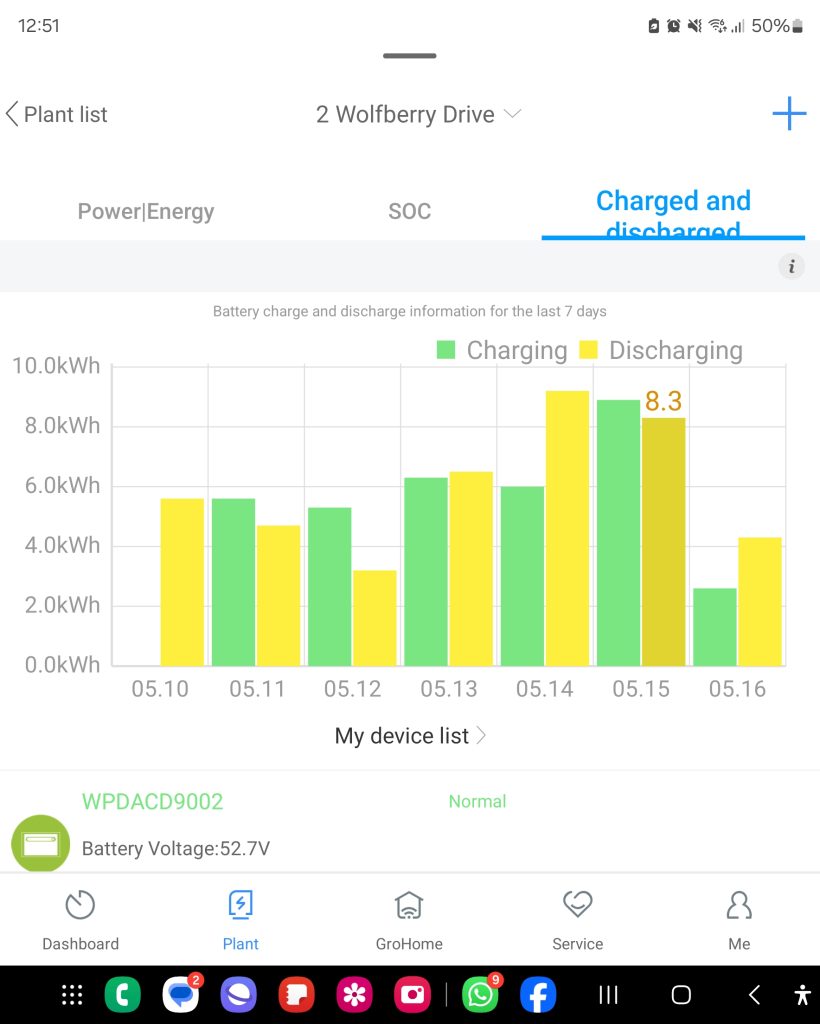
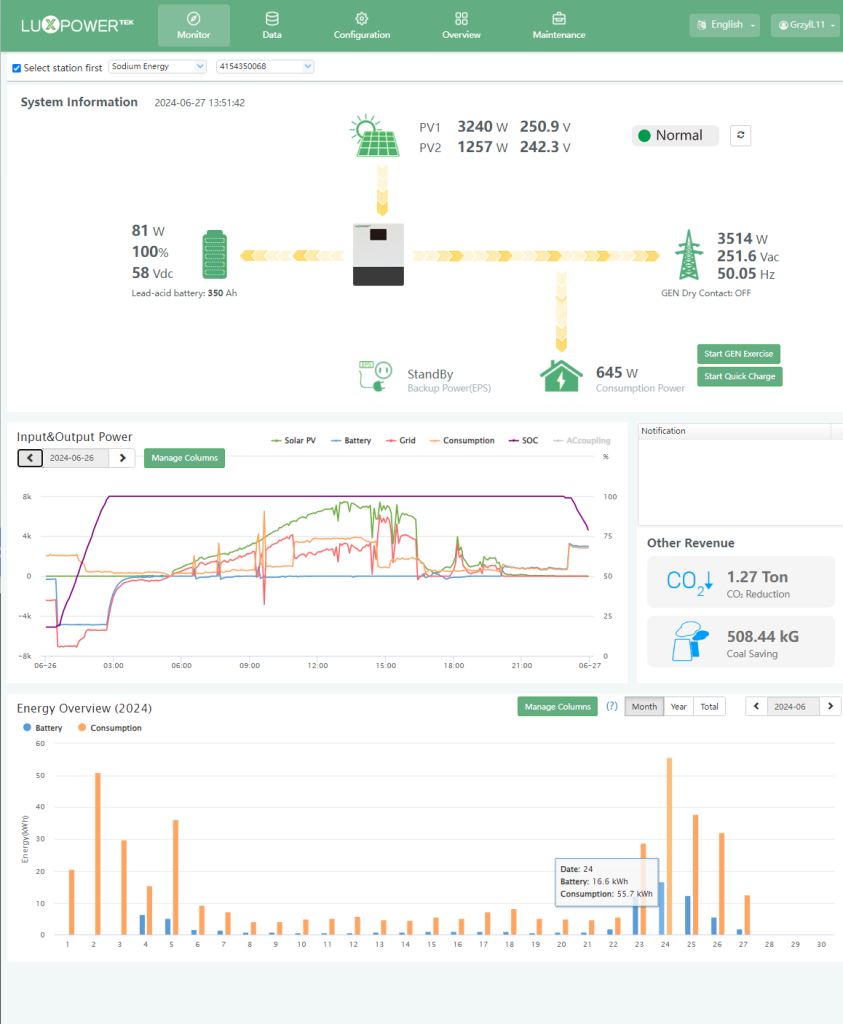
4.LUXPOWER LXP-LB-EU 7K 7kW Grid-Tied Hybrid Solar Inverter
- Hybrid Versatility: The LUXPOWER 7kW inverter showcased the versatility of our sodium batteries in a hybrid environment. It effectively managed high-power demands and provided robust support for both grid-tied and off-grid scenarios. The system's ability to handle peak loads without performance degradation underscored the robustness of sodium battery technology.
Key Takeaways
- Voltage Range and SOC Management: The broad voltage range of our sodium batteries simplifies SOC estimation, eliminating the need for BMS cables, which has historically been a point of failure in lithium battery systems.
- Compatibility and Integration: Sodium batteries have proven to be highly compatible with a range of inverters and chargers, offering flexibility for different energy storage solutions.
- Efficiency and Reliability: Across various tests, our sodium batteries have demonstrated excellent efficiency, reliable performance, and robust integration capabilities.
Minor Negatives
While the benefits of sodium batteries are clear, it's essential to acknowledge some minor drawbacks to provide a balanced perspective:
- Increased Weight and Size: Our sodium batteries are approximately 50% heavier and larger than comparable LFP units. This increased weight and size can be a consideration for installations where space and structural support are limited.
- Limited Utilization with Current Inverters: Most inverters operate within a 40-60V range, meaning some of our battery capacity isn't utilized. This results in around a 30% loss in overall capacity, although it does create a nice buffer. This issue will be addressed in our new model, which will have a voltage range of 36.4V to 58.8V, allowing for the utilization of 90% of capacity with currently available inverters.
Conclusion
Our six-month testing period has underscored the potential of sodium batteries as a viable alternative to traditional lithium-based storage solutions. Their unique characteristics, such as a wide voltage range and compatibility with diverse charging equipment, position them as a strong contender in the home battery storage market. Despite some minor negatives, such as increased weight and size and limited utilization with current inverters, the overall performance and reliability of sodium batteries make them an exciting option for sustainable energy solutions.
Stay tuned for more updates as we continue to push the boundaries of energy storage technology. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences with sodium batteries, feel free to drop us an email or reach out on our Facebook page.
